|
Amplitude Marginaliser
|
|
Amplitude Marginaliser
|
A set of functions for analytically marginalising a Gaussian likelihood ratio over signal model component amplitudes. More...
#include <math.h>#include <string.h>#include <gsl/gsl_math.h>#include <gsl/gsl_sf_erf.h>#include <gsl/gsl_randist.h>#include <gsl/gsl_rng.h>Go to the source code of this file.
Defines | |
| #define | AM_SQUARE(x) (x*x) |
| #define | AM_LN2PI (M_LN2 + M_LNPI) |
| #define | AM_LNPI_2 (M_LNPI - M_LN2) |
Functions | |
| double | marginalise_amplitudes (int Nmodels, double **modelModel, double *dataModel, double sigma, unsigned int lastHalfRange) |
| Marginalise a Gaussian likelihood ratio over the amplitudes for each of a set of model components. | |
| float | marginalise_amplitudes_f (int Nmodels, float **modelModel, float *dataModel, float sigma, unsigned int lastHalfRange) |
The same as marginalise_amplitudes(), but for float inputs rather than double. | |
| double | marginalise_amplitudes_except_final (int Nmodels, double **modelModel, double *dataModel, double sigma) |
| Marginalise over all amplitudes except for the final model component. | |
| float | marginalise_amplitudes_except_final_f (int Nmodels, float **modelModel, float *dataModel, float sigma) |
The same as marginalise_amplitudes_except_final(), but for float inputs rather than double. | |
| double | marginalise_amplitudes_linear (int Nmodels, double modelModel[], double dataModel[], double sigma, unsigned int lastHalfRange) |
The same as marginalise_amplitudes(), but with the modelModel array made into a 1D vector rather than a 2D array. | |
| double | marginalise_amplitudes_except_final_linear (int Nmodels, double modelModel[], double dataModel[], double sigma) |
The same as marginalise_amplitudes_except_final(), but with the modelModel array made into a 1D vector rather than a 2D array. | |
| double | marginalise_three_amplitudes (double **modelModel, double *dataModel, double sigma, unsigned int lastHalfRange) |
| Performs the likelihood ratio marginalisation explicitly written out for the model amplitude components. | |
| float | marginalise_three_amplitudes_f (float **modelModel, float *dataModel, float sigma, unsigned int lastHalfRange) |
The same as marginalise_three_amplitudes(), but for float inputs rather than double. | |
| double | marginalise_three_amplitudes_exclude_final (double **modelModel, double *dataModel, double sigma) |
| Explicitly marginalise over the first three model component amplitudes, but not the final one. | |
A set of functions for analytically marginalising a Gaussian likelihood ratio over signal model component amplitudes.
| #define AM_LN2PI (M_LN2 + M_LNPI) |
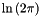 using GSL constants
using GSL constants
| #define AM_LNPI_2 (M_LNPI - M_LN2) |
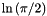
| #define AM_SQUARE | ( | x | ) | (x*x) |
The square of x
| double marginalise_amplitudes | ( | int | Nmodels, |
| double ** | modelModel, | ||
| double * | dataModel, | ||
| double | sigma, | ||
| unsigned int | lastHalfRange | ||
| ) |
Marginalise a Gaussian likelihood ratio over the amplitudes for each of a set of model components.
Function to marginalise over the amplitudes for each of the model components, where there can be an arbitrary number of models. In general all the amplitudes are marginalised between 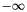 and
and 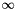 , although if specified the final model component amplitude will be marginalised between 0 and
, although if specified the final model component amplitude will be marginalised between 0 and 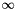 i.e. it's a purely positive model.
i.e. it's a purely positive model.
| Nmodels | - the number of components of the signal model with separate amplitudes |
| modelModel | - a 2D array containing the sums of the model cross products from the likelihood e.g. for three model components (see Description) 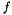 , , 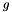 , , 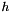 , this should contain: , this should contain:
|
| dataModel | - a 1D array containing the sums of the product of the data, 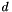 , with each model component from the likelihood e.g. , with each model component from the likelihood e.g. 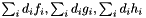 . . |
| sigma | - the noise standard deviation of the data. |
| lastHalfRange | - if this is set to 1 the final model component will be marginalised between 0 and infinity rather than the default of -infinity to infinity. |
Note: this function does not apply priors to the marginalised amplitudes, but flat prior values could be applied afterwards provided the likelihoods have approached zero towards the edges of the prior range.
| double marginalise_amplitudes_except_final | ( | int | Nmodels, |
| double ** | modelModel, | ||
| double * | dataModel, | ||
| double | sigma | ||
| ) |
Marginalise over all amplitudes except for the final model component.
This function allows for a model that contains components for which the amplitudes are required to be marginalisation over, and also a component (which could contain multiple components defined by various parameters itself) for which no marginalisation is required. It follows the same route as for marginalise_amplitudes(), but stops before the final marginalisation.
All the amplitude marginalisations are performed over the 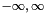 range.
range.
| double marginalise_three_amplitudes | ( | double ** | modelModel, |
| double * | dataModel, | ||
| double | sigma, | ||
| unsigned int | lastHalfRange | ||
| ) |
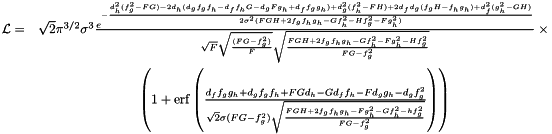
Performs the likelihood ratio marginalisation explicitly written out for the model amplitude components.
For three amplitudes the marginalised likelihood ratio is given by:
![\[ \mathcal{L} = (2\pi)^{3/2}\sigma^3 \frac{e^{-\frac{ d_h^2(f_g^2-FG) -2d_h(d_g f_g f_h - d_f f_h G -d_g F g_h + d_f f_g g_h) + d_g^2(f_h^2 - FH) + 2d_f d_g(f_g H - f_h g_h) + d_f^2(g_h^2 - GH)}{2\sigma^2 (FGH + 2f_g f_h g_h -G f_h^2 - H f_g^2 - F g_h^2) }}}{\sqrt{F}\sqrt{\frac{(FG - f_g^2)}{F}}\sqrt{\frac{FGH + 2f_g f_h g_h -G f_h^2 - F g_h^2 - H f_g^2}{FG - f_g^2}}} \]](form_40.png)
for an integral between 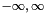 for all amplitudes, and
for all amplitudes, and
for the final integral being between ![$[0, \infty]$](form_42.png) . In these equations we have used the following substitutions:
. In these equations we have used the following substitutions: 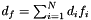 ,
, 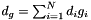 ,
, 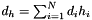 ,
, 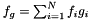
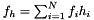 ,
, 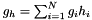 ,
, 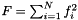 ,
, 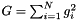 , and
, and 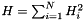 where
where 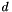 is the data and
is the data and 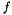 ,
, 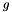 and
and 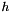 are the three model components for which the amplitudes have been marginalised over.
are the three model components for which the amplitudes have been marginalised over.
This function explicitly writes out the marginalised likelihood ratio for a model consisting of three components with the amplitudes marginalised over. This can be used to test the correctness of the marginalise_amplitudes() function.
| double marginalise_three_amplitudes_exclude_final | ( | double ** | modelModel, |
| double * | dataModel, | ||
| double | sigma | ||
| ) |
Explicitly marginalise over the first three model component amplitudes, but not the final one.
This function uses the fully expanded integral over the amplitudes of first three components of a signal model, whilst not integrating over the final fourth component's amplitude. All the amplitude marginalisations are performed over the 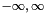 range. This can be used to test the correctness of the
range. This can be used to test the correctness of the marginalise_amplitudes_except_final() function.
 1.7.6.1
1.7.6.1